
Yemen is a country located in the southwest of the Arabian Peninsula. The capital of Yemen is Sana`a. The currency of this country is the Yemeni Rial and is known by the code YER. The official language of Yemen is Arabic and most of its people speak Arabic. Regarding religion, the majority of Yemeni people are Muslim and beliefs are divided between Shia and Sunni. Yemen is a country with an agricultural economy based on agriculture, processing industries, oil and natural gas, various industries and influential services. The products that Yemeni merchants import and export to other countries include food products such as coffee, honey, spices and fruits, textile and clothing products, wooden products and handicrafts, food products, chemicals and other products. Also, the export of oil and gas plays an important role in Yemen`s economy. You can get more information about the ways to contact Yemeni businessmen through the Yemeni embassy or consulate in your country. Also, visiting sites related to Yemeni companies and commercial organizations, consulting with business and economic experts or using communication methods such as phone calls and emails can also help you get more information.
-
 Amiraddin 4 months ago
Amiraddin 4 months ago Yemen
Jade Stone
Yemen
Jade Stone
Jade stone for saleDetails
-
 Samir Silan 3 months ago
Samir Silan 3 months ago Yemen
Transparent White Diamond
Yemen
Transparent White Diamond
Transparent White DiamondDetails
-
 Abu Shahab 3 months ago
Abu Shahab 3 months ago Yemen
Gemstone Needs
Yemen
Gemstone Needs
Peace be upon you ... What type of stone attracts magnetism?Details
-
 Ibrahim Al-Abrahimi 7 months ago
Ibrahim Al-Abrahimi 7 months ago Yemen
Gemstones Meteorites Minerals
Yemen
Gemstones Meteorites Minerals
Meteorite for saleDetails
-
 حافظ الجماعي 3 months ago
حافظ الجماعي 3 months ago Yemen
Governor of Yemen
Yemen
Governor of Yemen
The best types of meteorites in all colorsDetails
-
 Salem Al-Awlaqi 3 months ago
Salem Al-Awlaqi 3 months ago Yemen
Precious Stones
Yemen
Precious Stones
All kinds of precious stonesDetails
-
 Ahjar 3 months ago
Ahjar 3 months ago Yemen
Precious Stones
Yemen
Precious Stones
Everything is availableDetails
-
 Abdullah Mohammed Abdullah 3 months ago
Abdullah Mohammed Abdullah 3 months ago Yemen
Needs. Precious Stones. Antiques
Yemen
Needs. Precious Stones. Antiques
Nabzak stone and hexagonal diamond for sale 60,000 dollarsDetails
-
 Ahmad Alhamid 3 months ago
Ahmad Alhamid 3 months ago Yemen
The Meteor
Yemen
The Meteor
Gemstone ScientistDetails
-
 حجر نيزك قمري بريشيا 3 months ago
حجر نيزك قمري بريشيا 3 months ago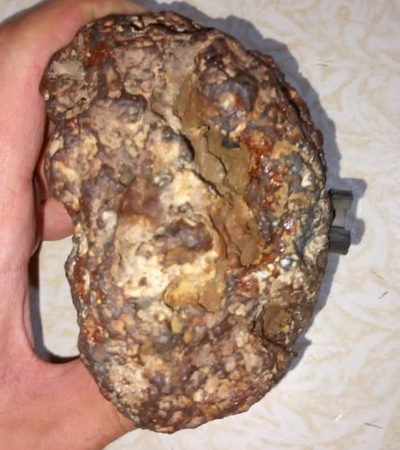 Yemen
Moon meteorite of Breccia type
Yemen
Moon meteorite of Breccia type
Moon meteorite of Breccia type. It is attracted to magnets. It has a shiny, glittering appearance, a beautiful shiny stone with the presence of iron m...Details
-
 Nasr Al-Falahi 3 months ago
Nasr Al-Falahi 3 months ago Yemen
Gemstones and Meteorite
Yemen
Gemstones and Meteorite
Heavy iron meteorite stone weighing approximately 258 grams, gemstonesDetails
-
 Ben Alajam 3 months ago
Ben Alajam 3 months ago Yemen
Meteorite
Yemen
Meteorite
High quality raw gemstonesDetails
-
 Ali Abdul Karim 7 months ago
Ali Abdul Karim 7 months ago Yemen
Platinum
Yemen
Platinum
Pure platinum stone with its certificateDetails
-
 Mohammad 3 months ago
Mohammad 3 months ago Yemen
Meteorite
Yemen
Meteorite
It was obtained on 2/1/2025. The meteorite has been confirmed to have a strong attraction with a magnet and is very heavy.Details
-
 Hajr Zink Nader Lelbaii Yumkinuk Altaasal Bina 4 months ago
Hajr Zink Nader Lelbaii Yumkinuk Altaasal Bina 4 months ago Yemen
We have a rare zinc stone for sale, you can contact us
Yemen
We have a rare zinc stone for sale, you can contact us
We have a rare zinc stone for sale, you can contact usDetails
-
 Dr. Abdullah 3 months ago
Dr. Abdullah 3 months ago Yemen
Precious Stones
Yemen
Precious Stones
The image is as it is in nature before it is polished or even washed, and there are other images of it for those who wish to contact (diamond)Details
Yemen’s trade dynamics in recent years reflect a challenging but evolving landscape, particularly for businesses aiming to engage with Yemeni exporters and importers in West Asia. According to WTO data, Yemen’s merchandise import value index fell from 110.6 in 2021 to 95.7 in 2023, significantly underperforming the global average of 101.1 in 2023. This decline signals reduced purchasing power and import demand, likely driven by economic instability and currency devaluation. However, the import volume index for 2023 (98.8) shows a modest recovery compared to 2022 (89.2), suggesting a gradual stabilization in trade flows. Global businesses should note this as a potential entry point for supplying essential goods to Yemen, particularly in sectors with consistent demand such as food, pharmaceuticals, and construction materials.
On the export side, Yemen has faced steep challenges. The merchandise export value index plummeted from 163.9 in 2021 to just 36.3 in 2023, far below the global average of 102.3. This sharp decline reflects disruptions in Yemen’s key export sectors, including oil and agricultural products. The export unit value index also dropped to 91.0 in 2023, compared to the global average of 95.0, indicating reduced competitiveness in international markets. However, Yemeni exporters active in West Asia may find opportunities in diversifying their product mix and targeting niche markets where local goods, such as coffee and honey, are highly valued.
Comparatively, Yemen’s economic structure is heavily reliant on agriculture, which accounted for an estimated 15.2% of GDP in 2023, higher than the global average of 11.4%. This over-reliance on agriculture, combined with underperforming industrial and service sectors, underscores the need for investment in industrial development and trade facilitation. For international investors, opportunities exist in sectors like renewable energy, logistics, and agro-processing, which can address Yemen’s structural gaps while offering long-term growth potential.
Despite these challenges, Yemen’s strategic location near key shipping routes in the Middle East presents a unique opportunity for businesses seeking to strengthen regional supply chain solutions. Platforms like Aritral.com can play a pivotal role in connecting Yemeni traders with global buyers, offering tools such as AI-powered international marketing and verified exporter profiles. By creating a business profile on Aritral.com, companies can gain visibility in West Asia’s competitive market and tap into Yemen’s resilient entrepreneurial base, which remains active despite economic hurdles.





















