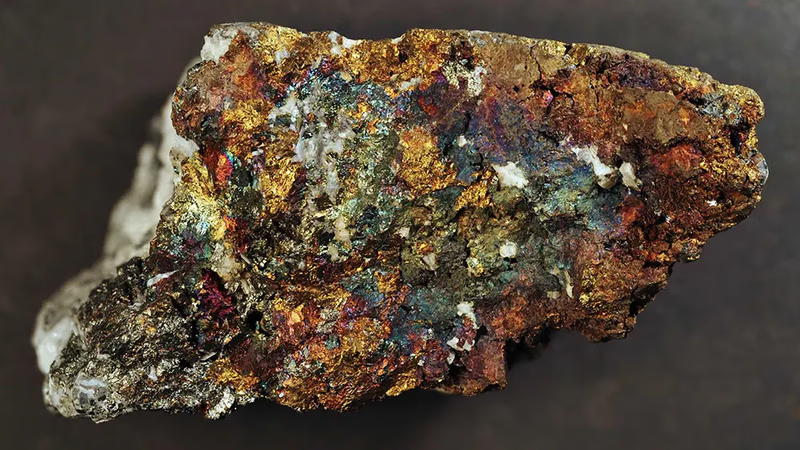
Chalcopyrite: A vital source of copper minerals.
Chalcopyrite or copper chalcopyrite is a copper mineral from which copper is extracted. Its scientific name is \"CuFeS2\" and it contains the elements copper (Cu), iron (Fe) and sulfur (S). Chalcopyrite is one of the most important copper minerals worldwide and is mostly found in copper sulphide mines. Chalcopyrite has a coppery yellow to coppery red color and has an algal or medium luster. It has a hardness of 2.5 to 3 on the mouse scale. Its density is about 4.1 to 4.3 grams per cubic centimeter. Its melting point is about 1,085 degrees Celsius. Chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) as one of the copper sulphide minerals, is the most widely used in the production of copper metal. Extraction of copper from chalcopyrite is done by flotation process. This process involves crushing minerals, adding special chemicals to them and separating copper minerals from other minerals. After separation, the copper is extracted from the chalcopyrite and refined using chemical and physical processes to convert it into pure copper metal.
Copper is extracted from chalcopyrite by a process called flotation. In this process, sulfide minerals are first crushed and then water and special chemicals are added to separate the copper minerals from other minerals. Then, using flotation technology, copper minerals are separated and a range of chemical and physical processes are used to purify and extract copper. Copper is used as an important industrial metal in many industries. Copper is very important as an electrical conductor and is used in the production of electrical wires and cables, transformers, electronic circuits and other components. Copper is used in the construction industry for water piping, heating and cooling systems, as well as in making decorative items and works of art. In the production of cars, copper is used in electrical systems, brake systems and other parts. Copper is used as an ornamental metal in making jewelry and ornaments.
In addition to chalcopyrite, copper may also be found in many other sulfide minerals. Bornite is also known as \"five-colored copper\" and has the chemical formula Cu5FeS4. Bornite is colorful and lustrous and occurs as crystalline masses or fine grains. Covelite has the chemical formula CuS and is mostly found as amorphous masses. Its color is usually dark blue to black and has a low gloss. Chalcocite has the chemical formula Cu2S and is found as opaque, dense and shiny crystals. Its color is usually dark gray to black. Other copper sulphide minerals include Tennantite, Enargite, Pyrite and Molybdenite. Each of these minerals has a different chemical formula and properties.
In addition to the previously mentioned copper sulfide minerals, copper may also be extracted from other minerals. Azurite mineral has the chemical formula Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2. This mineral is found as dark blue to blue-green and shiny crystals. Azurite is commonly used in copper production. Malachite has the chemical formula Cu2CO3(OH)2 and is found as dark green to pale green and shiny crystals. This mineral is also used as a source of copper. Cuprite has the chemical formula Cu2O and is found as dark red to red-brown and shiny crystals. This mineral can also be a source for copper extraction. Copper may be extracted in carbonate minerals such as malachite and azurite mentioned above.
The most important mineral for copper extraction is chalcopyrite (CuFeS2). Chalcopyrite is used as the main copper mineral in copper mines, and the largest amount of copper in the world is extracted from this mineral. Extraction of copper from chalcopyrite is done using flotation process and other chemical and physical processes to convert it into pure copper metal. Chalcopyrite is known as the most important mineral for copper production due to its abundance and richness in copper resources and relatively easy extraction and processing.
-

China and the United States are the largest consumers of chalcopyrite, with significant contributions from Peru, Germany, France, and Australia. Chalcopyrite reserves are abundant in countries like China, Peru, America, Zambia, Argentina, and Australia. In 2020, global copper extraction reached approximately 20. 6 million tons, with chalcopyrite being a key component. Major producers include Jiangxi and Freeport-McMoRan. The construction, automotive, and electronics industries heavily influence chalcopyrite consumption in these regions. Europe also plays a crucial role in consumption through countries like Germany and France. The demand-supply dynamics significantly affect chalcopyrite pricing; high demand with limited supply leads to price increases while the opposite results in price drops. Economic conditions and geopolitical factors further impact both supply and pricing of chalcopyrite.
-

Chalcopyrite serves as the primary source of copper, with its production closely tied to copper demand. As global economic growth accelerates, industries such as construction, automotive, electronics, and energy drive increased demand for both copper and chalcopyrite. Factors influencing this market include technological advancements, infrastructure development, and population growth. The price of copper significantly impacts chalcopyrite supply; rising prices can boost production while falling prices may hinder it. The construction sector is a major consumer of these minerals, with infrastructure projects further amplifying demand. Emerging sectors like clean energy and electric vehicles also contribute to the growing need for chalcopyrite. Regulatory changes regarding environmental practices can affect mining operations and supply levels. Innovations in extraction technologies enhance productivity and reduce costs while promoting sustainability through energy-efficient methods.
Recycling initiatives are crucial in preserving resources and minimizing reliance on new mining activities. The availability of alternative copper sources may also influence chalcopyrite demand; increased extraction from other minerals could lead to a decline in chalcopyrite"s market position. "
-
Chalcopyrite, scientifically known as CuFeS2, is a key copper mineral primarily used for copper extraction. It is characterized by its coppery yellow to red color and moderate hardness. The extraction process involves crushing the mineral, followed by flotation, where chemicals are added to separate copper from other minerals. This method allows for the purification of copper, which is essential in various industries including electrical, construction, and automotive sectors. Chalcopyrite"s significance lies in its abundance and efficiency in yielding copper compared to other sulfide minerals like bornite and covelite. The mineral"s properties make it a vital resource for producing pure copper metal, which is widely utilized in electrical wiring, plumbing systems, and decorative items. Other notable copper minerals include azurite and malachite, which also serve as sources for copper extraction but are less prominent than chalcopyrite. Overall, chalcopyrite remains the most important mineral for global copper production due to its rich deposits and straightforward extraction processes.
-

Chalcopyrite deposits in West Asia are crucial for the region"s copper market, influencing competitiveness against global resources. The density and quality of these deposits, along with mining and processing costs, play a significant role in their viability. Advanced extraction technologies and suitable infrastructure further enhance their competitiveness. The Middle East"s copper market is affected by global demand, pricing, and economic conditions, making the efficient extraction of chalcopyrite essential. Countries like Iran, Türkiye, and Iraq host significant chalcopyrite reserves that contribute to local employment and economic growth. Modern methods such as flotation and hydrometallurgical extraction are employed to maximize productivity while minimizing waste. The mining sector"s advancements also foster technological development and infrastructure improvements in the region. Overall, chalcopyrite mines are pivotal in meeting the Middle East"s copper needs and stabilizing supply within the market.