
Tourism in West Asia: Explore cultural heritage and natural beauty.
Several countries in West Asia have well-established tourist destinations that attract a large number of visitors. For example, Egypt is renowned for its ancient pyramids, historical sites, and the Nile River. Jordan is famous for the ancient city of Petra and the Dead Sea. The United Arab Emirates, particularly Dubai and Abu Dhabi, has emerged as a major tourist hub with iconic landmarks, luxury resorts, and entertainment attractions. Turkey, with its rich history and diverse landscapes, is a popular destination as well. West Asia is home to significant religious sites that attract millions of pilgrims and tourists each year. Saudi Arabia, for instance, welcomes millions of Muslims for the annual Hajj pilgrimage to Mecca and Medina. Iran attracts Shia Muslims to important religious sites such as Mashhad and Qom. Iraq also receives pilgrims visiting the holy cities of Najaf and Karbala. Religious tourism plays a significant role in the region's tourism industry and contributes to its overall economic growth.
Some West Asian countries have developed medical tourism as a thriving sector. Countries like Jordan, Israel, and the United Arab Emirates offer advanced medical facilities and expertise, attracting patients from around the world seeking specialized medical treatments, surgeries, and wellness services. Medical tourism contributes to the region's tourism industry and helps generate revenue. West Asia is home to diverse landscapes and natural attractions. Countries like Oman, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates offer opportunities for desert safaris, dune bashing, and outdoor adventures. Oman's mountains, wadis, and beaches attract nature enthusiasts and adventure seekers. These countries are developing nature-based tourism to diversify their offerings and attract visitors interested in ecotourism and outdoor activities.
Three countries, Saudi Arabia, Egypt and Morocco, ranked first among the Arab countries in the region in attracting tourists. The total number of foreign tourists in the Middle East in 2012 was reported at 52 million, a decrease of 5% due to tensions and unrest in the region. Egypt was able to re-establish itself among the tourist countries in 2012 with an 18% growth rate, after overcoming the turbulent period that led to the fall of the "Hosni Mubarak" regime and the overall security situation in the country.
The tourism industry in West Asia, also known as the Middle East, has experienced significant growth and has become an important sector for many countries in the region. The level of the tourism industry varies across countries, with some nations having well-established tourism sectors while others are still developing their tourism infrastructure. It's important to note that the tourism industry in West Asia has faced challenges due to geopolitical conflicts, security concerns, and regional instability. However, many countries are actively working to enhance their tourism infrastructure, promote their unique attractions, improve visa processes, and enhance visitor experiences to attract more tourists and diversify their economies.
West Asia, with its modern infrastructure and business-friendly environments, has become a popular destination for business and MICE (Meetings, Incentives, Conferences, and Exhibitions) tourism. Cities like Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Doha, and Riyadh host international conferences, exhibitions, and corporate events, attracting business travelers from around the world.
West Asia boasts a rich cultural heritage and historical sites that draw tourists interested in archaeology, ancient civilizations, and cultural experiences. Countries such as Iran, Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, and Iraq have numerous UNESCO World Heritage sites, including Persepolis, Luxor, Petra, Baalbek, and Babylon, respectively. These attractions contribute to the tourism industry and help promote cultural understanding and heritage preservation. The United Arab Emirates, particularly Dubai, has positioned itself as a global entertainment and shopping destination. The city offers luxury shopping malls, theme parks, world-class hotels, and entertainment venues. It hosts international events, such as the Dubai Shopping Festival and Dubai Expo, attracting tourists seeking leisure, entertainment, and shopping experiences.
-

West Asia, rich in oil and gas reserves, plays a crucial role in the global energy market. Countries such as Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, the UAE, and Qatar are key suppliers of these resources, which significantly contribute to their economic growth. The revenue from energy exports has enabled substantial foreign exchange reserves and funding for infrastructure development and social welfare programs. Additionally, West Asian nations have diversified their economies by investing in sectors like petrochemicals and tourism. Sovereign wealth funds (SWFs) established by these countries manage surplus funds and invest globally, enhancing financial market stability. Despite the dominance of oil and gas, there is a growing focus on agriculture to ensure food security. Countries like Saudi Arabia and Qatar are implementing agricultural technologies to boost local production. The region"s strategic location has attracted foreign investment and trade opportunities, with nations developing industrial zones and free trade areas to facilitate business activities. Overall, West Asia"s economic landscape is shaped by its energy resources while also adapting to new challenges through diversification.
-

Commodity exchanges play a crucial role in facilitating trade across Asia, particularly in the Middle East and West Asia. With 10 of the 22 major commodity futures exchanges located in Asia, these platforms enable buyers and sellers to engage in trading various commodity contracts. The Dubai Commodity Center, established in 2002, exemplifies the region"s commitment to creating a robust infrastructure for commodity trading. The Dubai Gold and Commodity Exchange is notable for its automated trading of derivatives for commodities like gold and silver, operating primarily in US dollars. This exchange has positioned Dubai as a global hub for financial markets. Additionally, the Dubai Mercantile Exchange has gained prominence as a key energy market since its inception, although competition has emerged with the Shanghai Energy Exchange. In Iran, the Commodity Exchange operates under specific regulations that require brokers to manage purchase orders meticulously. Turkey"s stock market history dates back centuries, with modern exchanges evolving significantly over time. Overall, these exchanges not only facilitate local trade but also connect regional markets to global commodity networks.
-

West Asian governments are actively pursuing economic diversification to reduce reliance on oil revenues. They are investing in various sectors, including manufacturing, tourism, finance, technology, renewable energy, and agriculture. By establishing industrial zones and promoting local production capabilities, these countries aim to boost exports and attract foreign direct investment (FDI). The development of financial sectors into regional hubs is also a priority, with efforts to promote Islamic finance and expand capital markets. A skilled workforce is essential for this transition; thus, investments in education and vocational training are being made. Renewable energy projects are gaining traction as countries seek to harness solar and wind power for clean energy production. While non-oil goods currently play a minor role in the economy compared to other regions, their importance is expected to grow significantly. The shift towards an oil-independent economy involves long-term strategies that require sustained policy reforms and investments.
Additionally, the tourism sector is being developed due to the region"s rich cultural heritage and natural attractions. Knowledge-based industries such as IT and R&D are also being prioritized through the establishment of technology parks and support for startups. Overall, West Asia is making strides towards a more diversified economic landscape that can sustain growth beyond oil. "
-

West Asia, primarily known for its oil-dependent economies, faces significant challenges due to its reliance on crude oil exports. Countries like Saudi Arabia, Iraq, and the UAE have historically depended on oil revenues for economic stability and growth. This overreliance has hindered diversification into other sectors such as manufacturing and services, making these economies vulnerable to global market fluctuations and political instability. In response, many nations are initiating economic diversification strategies aimed at reducing dependence on oil. The UAE exemplifies this shift by investing in tourism, finance, and renewable energy. Additionally, sovereign wealth funds are being established to invest oil revenues in international markets for long-term stability. As the region recognizes the need for sustainable energy solutions, investments in renewable projects are increasing. Despite these efforts, the World Bank forecasts modest economic growth for oil-exporting countries in 2021 due to ongoing challenges in global demand and production agreements. The heavy reliance on oil continues to shape fiscal policies and government budgets across West Asia, with fluctuations in oil prices posing risks to economic stability.
-
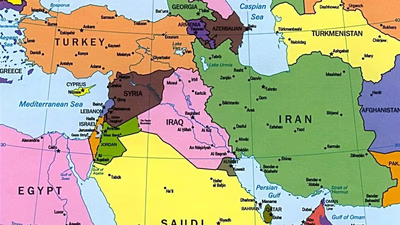
West Asia"s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe, Africa, and Asia makes it a vital hub for trade and communication. The region is rich in oil and natural gas reserves, significantly influencing global energy markets and prices. However, West Asia faces security challenges, including political instability and conflicts that have international repercussions. Water scarcity is another pressing issue affecting agriculture and livelihoods. The Middle East serves as a critical link between continents, with key maritime routes like the Suez Canal and the Strait of Hormuz enhancing its geopolitical importance. Historical influences from global powers have contributed to regional instability but also fostered diplomatic initiatives aimed at conflict resolution. Economically, West Asian countries have experienced rapid growth driven by oil revenues, attracting foreign investment across various sectors such as finance and tourism. The region"s cultural heritage, being the birthplace of major world religions and home to significant historical sites, further enhances its global significance.
-

West Asia"s economies are primarily driven by the oil and gas sector, with major producers like Saudi Arabia, Iraq, and Iran leading in exports. These countries have heavily invested in petrochemical industries, producing a range of chemical products. However, there is a growing shift towards renewable energy sources as nations like the UAE and Jordan commit to solar and wind projects to diversify their energy portfolios. The region is also experiencing a boom in the information technology sector, particularly in Israel and Turkey, focusing on software development and cybersecurity. Manufacturing is being promoted across various industries to reduce oil dependency, with significant advancements noted in automotive and electronics. The construction sector has seen rapid growth due to urbanization and investment, particularly in the UAE and Qatar. Innovative agricultural practices are being adopted to enhance food security despite challenging climatic conditions. Additionally, West Asia"s financial sectors are robust, with cities like Dubai emerging as key financial hubs. Overall, West Asia is diversifying its economy while maintaining its traditional strengths.
-

West Asia"s tourism industry is diverse, with countries like Egypt, Jordan, and the UAE attracting millions of visitors. Egypt"s ancient pyramids and Jordan"s Petra are major draws, while the UAE has become a hub for luxury tourism. Religious tourism is significant, with Saudi Arabia hosting millions for Hajj and Iran attracting Shia pilgrims. Medical tourism is also growing in countries like Jordan and Israel, offering advanced healthcare services. The region"s natural landscapes provide opportunities for ecotourism, particularly in Oman and Qatar. Despite challenges from geopolitical tensions, many nations are enhancing their tourism infrastructure to attract more visitors. Business tourism is thriving in cities like Dubai and Doha, which host international events. Cultural heritage sites across the region contribute to its appeal, with numerous UNESCO World Heritage sites promoting cultural understanding.
Overall, West Asia"s tourism sector is evolving and plays a crucial role in economic growth. "







