
UAE"s diverse population reflects its vibrant trade landscape. "
Emiratis are the native population of the UAE and make up a relatively small percentage of the total population. Emirati citizens enjoy certain privileges and benefits provided by the government, including access to social welfare programs and employment opportunities in the public sector. The majority of the UAE's population consists of expatriate workers who come from various countries around the world. These individuals are attracted to the UAE for job opportunities, particularly in sectors such as construction, finance, hospitality, healthcare, and transportation. Expatriates come from diverse backgrounds, including South Asia (India, Pakistan, Bangladesh), other Arab countries (Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon), the Philippines, Western countries, and African nations.
According to the latest census in the UAE, which dates back to 2013, the country has a population of more than 9 million, of which only 1.4 million are from the UAE and the rest of the population are foreigners. Most foreigners in this country are Iranians, Europeans, Pakistanis, and Chinese. The UAE is one of the most immigrant-friendly countries and ranks fifth in the world in this regard, which is why, according to estimates, the population of this country will soon reach 10 million.
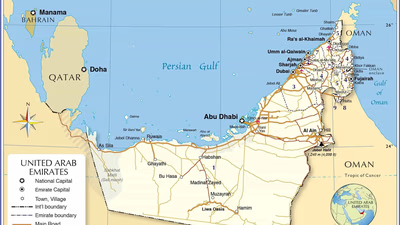
If we want to talk about the area and population of the UAE, we need to take a look at the geographical location of the country. The United Arab Emirates is located in the Middle East and is connected to the Persian Gulf from the north and northwest. Oman, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar are also neighbors of the United Arab Emirates. The country covers an area of 83,600 square kilometers and is ranked 115th in the world in terms of breadth. The United Arab Emirates is divided into seven sheikhdoms, which are:
- Abu Dhabi
- Dubai
- Sharjah
- Ajman
- Umm Al Quawain
- Head of Al-Khaimah
- Fujairah
Each of these areas has unique characteristics and special conditions. It is because of these seven sheikhdoms that this country is called the United Arab Emirates because the word UAE means sheikhdom or emirate, and when these seven zones are placed together, a united country is created. Come on. The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has a diverse demographic composition due to its status as a global hub for business, tourism, and employment opportunities. It's important to note that the demographic composition of the UAE is subject to change due to factors such as government policies, economic conditions, and global events. The UAE government has implemented various measures to manage population growth and maintain a balance between the native Emirati population and the expatriate workforce.
The UAE has a significant population of Arab expatriates from countries such as Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, and Yemen. Many of these individuals work in professional roles or own businesses in sectors like finance, education, and healthcare. South Asian countries, including India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka, contribute a large number of expatriate workers to the UAE. They are employed in various sectors and play a vital role in the country's economy. The UAE also attracts a substantial number of expatriates from Western countries, including the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia. These individuals often work in executive positions, finance, education, and other professional sectors.
-
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is a federation of seven emirates located in the Middle East, known for its significant oil reserves and economic diversification efforts. The country has transformed into a global business hub, with Dubai recognized for its tourism and architectural marvels. Abu Dhabi, the capital, features cultural landmarks like the Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque. The UAE"s economy is bolstered by sectors such as finance, real estate, and renewable energy, attracting international companies due to its transparency and security. The multicultural society comprises both Emiratis and expatriates, with Arabic as the official language and English widely spoken in business contexts. The UAE"s strategic geographical location enhances its role in regional trade, making it a vital player in West Asia"s import-export activities. Hosting major events like Dubai Expo 2020 and international sports competitions further solidifies its status as a trade advertising platform. Understanding the UAE"s unique characteristics is essential for businesses looking to engage in commodity trade or supply chain solutions within the region.
-

The UAE"s economy has historically depended on oil and gas revenues, but significant efforts have been made to diversify into sectors like tourism, finance, and technology. The government aims to create a sustainable economy by reducing reliance on petroleum exports. Dubai stands out as a regional financial center with a robust logistics network that enhances global trade connectivity. Despite diversification, oil still plays a crucial role in the economy, particularly in Abu Dhabi. The UAE ranks among the top exporters and importers globally, with strong trade ties to countries like China and India. The tourism sector has become a major non-oil income source, supported by luxury hotels and extensive development projects. The UAE actively seeks foreign investment through favorable policies and free zones that offer tax exemptions and 100% foreign ownership. This openness has fostered an environment conducive to international business growth, making the UAE a key player in global trade. "
-

The UAE has established comprehensive laws and regulations for imports and exports to facilitate trade while ensuring public health and safety. Customs duties vary based on product type, origin, and trade agreements, necessitating consultation with the Federal Customs Authority for accurate tariff rates. The UAE adheres to international sanctions, requiring compliance from all traders. Free zones offer benefits like 100% foreign ownership and tax exemptions, but regulations differ across emirates. Businesses must secure valid commercial licenses and register with the UAE Customs Office to operate. The country has a high import rate, primarily in precious metals and machinery, with specific tariffs on goods like alcohol (50%) and tobacco (100%). The UAE"s efficient trade processes make it one of the easiest countries for import-export activities in the region. Compliance with health standards is crucial for food and agricultural imports, often requiring certifications or inspections.
Intellectual property laws are robust, necessitating respect for trademarks and copyrights in trade activities. Importers must also navigate documentation requirements for customs clearance, including invoices and permits. "
-

Dubai has emerged as a pivotal international trade hub in the Middle East, particularly for Iranian traders. Its strategic location, coupled with advanced port and airport facilities, facilitates efficient import and export operations. The city is known for its diverse export activities, including agricultural products like fruits and nuts, as well as handicrafts. Exports to Dubai can be conducted via air or sea, with the latter often utilizing traditional dinghy methods due to their cost-effectiveness and speed. This method is particularly favored for non-sensitive goods that can withstand exposure to water. Despite Dubai"s economic strength, its agricultural sector is limited, leading to a reliance on imports for most summer crops from countries like Iran and Turkey. The fruit market in Dubai has become especially lucrative for Iranian exporters, with watermelon and tomatoes being among the top exported items. Overall, the trade dynamics in Dubai highlight its role as a vital B2B marketplace in West Asia. "
-

The UAE"s population exceeds 9 million, with Emiratis constituting a small fraction. The majority are expatriates drawn from diverse regions, including South Asia, the Middle East, and Western countries. This demographic diversity is fueled by the UAE"s status as a global business hub, offering numerous job opportunities in sectors like construction, finance, and healthcare. The government provides Emirati citizens with social welfare benefits and public sector employment opportunities. The population dynamics are influenced by government policies aimed at balancing the native Emirati population with the expatriate workforce. As a result, the UAE ranks fifth globally in terms of being immigrant-friendly. The country is geographically located in the Middle East and consists of seven emirates: Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ajman, Umm Al Quwain, Ras Al Khaimah, and Fujairah. Each emirate has unique characteristics that contribute to the overall economic landscape of the UAE. With ongoing changes in global conditions and local policies, the demographic composition of the UAE is expected to evolve further.
-

Abu Dhabi, the capital of the UAE, is the largest emirate and serves as the political and cultural hub. Known for its stunning architecture, it features landmarks like the Sheikh Zayed Grand Mosque and Emirates Palace. Dubai, the most populous city, is a global business center famous for its luxurious lifestyle and iconic structures such as Burj Khalifa. Other emirates like Ras Al Khaimah offer outdoor activities with mountainous landscapes, while Fujairah is popular for diving due to its rich marine life. Each emirate contributes uniquely to the UAE"s economic landscape, showcasing a blend of modernity and tradition. The UAE"s diverse cities enhance its appeal as a trade platform in West Asia, attracting both importers and exporters.






