
Saudi Arabia"s trade dynamics: oil exports and economic diversification. "
GDP is a measure of the total value of goods and services produced within a country's borders in a specific period. Saudi Arabia has a significant GDP, primarily driven by its oil industry. The non-oil sector has been a focus of diversification efforts under Vision 2030. Saudi Arabia is one of the world's leading oil producers and exporters. The volume of oil production and the revenue generated from oil exports significantly impact the country's economy and fiscal position. As part of the Vision 2030 plan, Saudi Arabia aims to reduce its dependency on oil and diversify its economy. The growth and performance of non-oil sectors, including manufacturing, construction, services, and tourism, are crucial indicators of economic diversification.
he trade balance represents the difference between a country's exports and imports. Saudi Arabia's trade balance is greatly influenced by its oil exports and the value of imports, including goods and services. The government's revenue and expenditure reflect its fiscal position and spending priorities. Revenue sources include oil revenues, taxes, and other sources, while expenditure covers areas such as infrastructure development, social welfare programs, and public services. The ease of doing business index assesses the regulatory environment and business-friendly policies in a country. Saudi Arabia has taken steps to improve its business environment, aiming to attract investment and foster entrepreneurship.
- Export amount of Saudi Arabia
Despite the large Oil exports, Saudi Arabia is not among the top 20 exporting countries in the world but is ranked 22nd after India. - The dairy industry of Saudi Arabia
It may seem strange to you, but the largest dairy factory is located in this country. 95,000 lactating cows are kept in this factory. Saudi Arabia produces one billion liters of milk daily. - Per capita income of Saudi Arabia
Per capita income in Saudi Arabia until the end of 2017 was equivalent to 59 thousand 170 dollars per year. This is 2.9 times less than the per capita income of American citizens. - Foreign immigration of Saudi Arabia
There are currently six million foreign nationals working in Saudi Arabia, and it is estimated that 15% of the country's total population are foreigners. - The unemployment rate of Saudi Arabia
Despite its economic size, Saudi Arabia also has one of the highest unemployment rates in the region. The country's unemployment rate in 2018 reached 12.9 percent. - The most profitable company in the world is in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Aramco is the world's most profitable company with a reported profit of $ 111 billion in 2018. The state-owned Oil company also had a higher net income than Apple Corps, Amazon, and Alphabet. Although Oil now accounts for 90% of its economy, no Oil had been discovered there until 1938.
Although Saudi Arabia is said to be rich in what it calls the world's second-largest Oil reserves, no Oil was discovered before 1938. It was not until 1938 that the Oil exploration team of a California Oil company discovered one of Saudi Arabia's Oil reserves. The California Oil company was in charge of managing Saudi Oil production until 1980, the Saudi dynasty took over. More than 90 percent of Saudi Arabia's national wealth now comes from Oil production.
The unemployment rate reflects the percentage of the labor force that is without employment and actively seeking work. Reducing unemployment and creating job opportunities for Saudi nationals is a key objective of the government's economic policies. Inflation measures the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is increasing and, consequently, eroding purchasing power. Controlling inflation is essential for maintaining price stability and ensuring the overall health of the economy. FDI refers to investments made by foreign entities in Saudi Arabia. FDI is a measure of investor confidence in the country's economy and can contribute to economic growth, job creation, and technology transfer.
Saudi Arabia's position in the list of GDP per capita in the Middle East, although Saudi Arabia ranks 18th in the world in terms of GDP, it ranks fourth in the Middle East in this regard. It houses the largest farm in the world, Al-Mara's farm in Saudi Arabia is the largest dairy farm in the world. On this farm, about 95,000 lactating cows are kept and about one billion liters of milk are produced daily. The annual income of an American is more than twice the annual income of a Saudi, In 2017, the annual income of each American was $ 56,160. While the annual income of each Saudi was $ 20,090 in the same year, which is 9.2 times lower than the annual income rate in the United States. One of its Oil fields has enough Oil that can fill 77.4 million swimming pools for the Olympics.
-

Saudi Arabia"s economy is heavily reliant on its vast oil reserves, managed by Saudi Aramco, the world"s largest oil company. The country holds over 260 billion barrels of oil, accounting for more than 14% of global reserves. Beyond oil, Saudi Arabia has developed a robust petrochemical sector and invested in infrastructure projects to diversify its economy. The agricultural sector has also seen advancements through modern irrigation techniques, enabling the cultivation of crops despite the arid climate. Additionally, the manufacturing industry is growing, focusing on steel, aluminum, and pharmaceuticals. The government promotes industrialization and local industries while also exploring its mineral resources like gold and copper. With a significant portion of its budget allocated to public employment and subsidies, Saudi Arabia"s economic structure is influenced by oil revenues. However, there is an ongoing need for economic reform as fluctuations in oil prices impact government spending.
The Vision 2030 initiative aims to reduce dependence on oil by fostering sectors such as tourism and technology while attracting foreign investment. This diversification strategy includes establishing economic zones to enhance trade opportunities. "
-
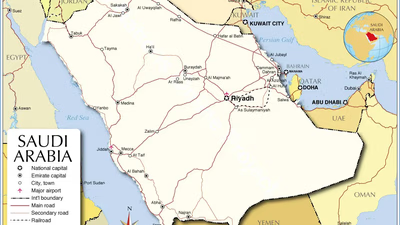
Saudi Arabia, the largest country in West Asia, occupies most of the Arabian Peninsula and is bordered by several nations including Jordan, Iraq, and Yemen. Its capital is Riyadh. The region is significant for its historical, cultural, and geopolitical importance, serving as a crossroads for Asia, Africa, and Europe. Saudi Arabia is rich in natural resources, particularly oil and gas, which dominate its economy—oil accounts for 95% of exports and 70% of government revenues. The country has seen rapid modernization due to extensive oil revenues. Additionally, Saudi Arabia has the sixth-largest natural gas reserves globally. The Middle East"s diverse landscapes include deserts and fertile valleys, with a complex geopolitical landscape shaped by various conflicts. The region is also culturally rich, home to numerous ethnic groups and languages.
Saudi Arabia"s historical significance includes being the birthplace of Islam and hosting important religious sites such as the Kaaba and the Prophet"s Mosque. "
-

Saudi Arabia"s economy is heavily influenced by its oil industry, which accounts for 90% of its GDP. The country is a leading oil producer and exporter, but it ranks 22nd globally in total exports. Efforts under Vision 2030 aim to diversify the economy by boosting non-oil sectors such as manufacturing, construction, and tourism. The trade balance is significantly affected by oil exports and imports of goods and services. Despite its economic size, Saudi Arabia faces challenges like a high unemployment rate of 12. 9% as of 2018 and lower per capita income compared to the U. S. Additionally, foreign direct investment (FDI) reflects investor confidence in the economy, contributing to growth and job creation.
The ease of doing business index indicates improvements in the regulatory environment to attract investments. Saudi Aramco stands out as the world"s most profitable company, showcasing the dominance of the oil sector in Saudi Arabia"s fiscal landscape. "
-

Saudi Arabia"s transport infrastructure is diverse, featuring extensive road networks, air travel, railways, and maritime routes. Road transportation is the most prevalent mode, with modern highways connecting major cities and facilitating both passenger and freight movement. The country boasts several international airports that serve as key hubs for global connectivity. Public transportation systems, including buses and metro networks in cities like Riyadh, enhance urban mobility. The railway network has expanded significantly since its inception in 1951, now totaling 2,785 kilometers and supporting both passenger and cargo services. Notably, the railway facilitates the transport of goods such as petroleum products and grains between key locations. Maritime transport also plays a crucial role in trade, with several major seaports enabling import and export activities. Overall, Saudi Arabia"s transport systems are integral to its economic growth and trade dynamics.
-

Saudi Arabia enforces strict regulations on the importation of various goods, primarily due to cultural and religious beliefs. Prohibited items include alcohol, pork, illegal drugs, firearms, and pornographic materials. The country also restricts the import of certain animals and animal products, gambling devices, counterfeit goods, and materials that contradict Islamic values. Additionally, specific medications may require special permits for importation. Despite these regulations, smuggling remains a challenge, with significant quantities of prohibited items being intercepted at borders. Understanding these restrictions is crucial for businesses engaged in trade within the region to ensure compliance and avoid legal issues.
-

Saudi Arabia enforces strict regulations on the import and export of goods to ensure compliance and safety. Customs authorities are responsible for inspecting cargo, verifying documentation, and enforcing restrictions. If violations are detected, a security label is affixed to the consignment, which is then stored by the shipping company until the owner can retrieve it in the presence of a customs inspector. In cases where the owner does not claim the cargo, it may be transferred to a designated location for further inspection. High-risk shipments undergo physical inspections at ports or airports to verify compliance with regulations. Customs authorities meticulously review shipping documents for accuracy; discrepancies can lead to penalties or further investigations. Serious violations may result in confiscation of goods, legal proceedings, and potential forfeiture. The enforcement of these laws is crucial for maintaining trade integrity within Saudi Arabia"s B2B marketplace and regional trade dynamics. "






