Kuwait"s rich history enhances its role in Middle East trade. "
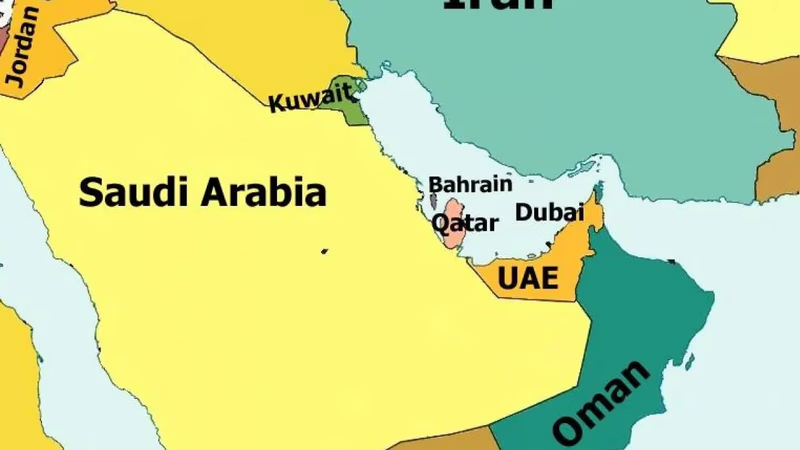
Kuwait is neighboring Saudi Arabia and Iraq, the country is smaller in size than all of its neighbors and sometimes smaller than one of their provinces, but its reputation around the world is complex. What are the characteristics of Kuwait that we hear its name from time to time? Residents of the southern cities of our country may know more about Kuwait. Kuwait is a country in West Asia. Kuwait has land borders with Iraq and Saudi Arabia and water borders with Iran via the Persian Gulf. Its capital is the city of Kuwait. The official language of this country is Arabic and its currency is the Kuwaiti Dinar. Of all Kuwaitis, 60% are Arabs and about 38% of Kuwaitis are of Asian descent.
The people of Kuwait are white and of Semitic descent, and among them are other Arab races such as the Adnan's (the first nomadic group from Najd to this land belonged to the Anza tribe) and the Qahtanis. The official language of Kuwait is Arabic. In addition, English is now of special importance due to the history of the British presence in this country and also the presence of the United States as a second language. The date of the founding of Kuwait goes back to Sheikh Barak ibn Gharir al-Hamid, the sheik of the Bani Khalid tribe and the ruler of the Emirate of Ehsa, who at the end of 1110 AH built a fort called Kut to store food and also store weapons, after which Kuwait took its name. And then this city was given to the Al-Sabah family during the time of Sheikh Sa'dun bin Muhammad Al-Hamid.
Kuwait in ancient times was mostly done by Iranians, especially the people of Bushehr and Khuzestan. At the beginning of the city's growth, several hundred Behbahani families from all walks of life settled in this port. Kuwait has five provinces in terms of administrative division, each of which is governed by a governor appointed by the emir. These five provinces are Central Province (Al-Asma), Al-Houli Province, Al-Ahmadi Province, Al-Jahraa Province, and Al-Farwaniyah Province. Kuwait is geographically a small country with an area of more than 17,000 square kilometers. It shares borders with Saudi Arabia and Iraq on land and with Iran by sea.
The climate of Kuwait is not unlike that of the scorching deserts of Saudi Arabia, and in most parts of the country, the climate is very hot and dry. It also has very little access to fresh water. This has led Kuwait to import many of its food and agricultural products. Even in recent years, the country has supplied part of its drinking water through imports and desalination plants. Of course, in recent decades, Kuwait has tried to slightly improve its agricultural situation by building greenhouses and changing farmland. Kuwait, despite its small size, is divided into six different provinces: Hooli, Jahra, Asma, Farwaniya, Ahmadi, and Mubarak al-Kabir.
Politically, Kuwait, like other countries in the Persian Gulf, is a sheikhdom. However, the political climate in this country is usually more open than in other Persian Gulf countries. The country gained independence in 1961, and since then several members of the Al-Sabah family have come to power in Kuwait. There is also a parliament in the country that oversees the activities of the government alongside the judiciary. Historically, the first steps in the establishment of Kuwait were taken by the Al-Hamid and Al-Sabah families. However, Iraq has always made claims to its territory that led to the second Persian Gulf War. Currently, Kuwait is one of the safest countries in the region and has good relations with many countries in the world.
-

Kuwait"s trade landscape is heavily dominated by petroleum exports, which account for approximately 92% of its total exports. The primary markets for these oil exports are Asian countries, notably China and India. In addition to oil, Kuwait also exports chemicals, fertilizers, and plastics. The country benefits from its membership in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), which fosters economic integration and trade cooperation among member states. Kuwait has established free trade zones, such as the Shuwaikh Free Trade Zone, to attract foreign investment and streamline customs processes. Despite a strong export economy, Kuwait relies on imports for many goods, including machinery, food products, and medical equipment. Major import partners include the United States, China, Germany, and India. Recent data indicates a notable increase in Iranian goods exported to Kuwait in 2018, highlighting shifts in trade dynamics within the region. Overall, while oil remains the cornerstone of Kuwait"s economy, the country is actively engaging in diversifying its trade relationships and enhancing its import capabilities.
-

Kuwait, located in the northeastern Arabian Peninsula, is bordered by Iraq and Saudi Arabia. With a population of approximately 4. 3 million, it features a mix of Kuwaiti citizens and expatriates. The capital, Kuwait City, serves as the political and economic hub. While not a major tourist destination, Kuwait offers attractions like the Kuwait Towers and Grand Mosque. The country has a strong economic presence in the region due to its strategic location and access to international waters. It is known for its high-value currency, the Kuwaiti Dinar (KWD), and well-developed infrastructure including roads, airports, and seaports. Kuwait"s economy is heavily reliant on oil exports but is diversifying into finance, real estate, and trade sectors.
The cultural landscape is influenced by Islamic traditions and Arab customs, with a significant expatriate community contributing to its demographic diversity. Understanding Kuwait"s market dynamics can benefit businesses looking to engage in import-export activities.
-

Kuwait"s economy is heavily influenced by Islam, which shapes its cultural and legal frameworks. The Kuwaiti Dinar (KWD) is the official currency, known for its high value linked to the oil sector. Approximately 70% of the population are Sunni Muslims, with a significant emphasis on charitable giving through zakat. The economy relies predominantly on oil exports, accounting for about 85% of government revenue. Despite this dependency, Kuwait is pursuing economic diversification to reduce reliance on oil and enhance sectors like finance and tourism. The country has implemented fiscal reforms in response to fluctuating oil prices, aiming to stabilize its economy. Agriculture plays a minimal role in GDP, making Kuwait a major food importer. The stability of Kuwait"s economy attracts global business actors, fostering a favorable environment for trade and investment.
Additionally, Islamic finance is prominent in Kuwait, offering Sharia-compliant financial products that align with religious principles. Religious tourism also contributes to the economy as visitors come to explore its historical Islamic sites.
-

Kuwait"s economy is heavily reliant on crude oil exports, which constitute 90% of its GDP and 75% of government revenue. The aftermath of the Gulf War in 1990 severely impacted its economic structure, leading to significant foreign investment efforts to revitalize the economy. Key exports to Kuwait include mineral products like gypsum and cement, iron and steel, live animals, food products, vegetables, fish, fruits, and building materials. The country has a relatively high per capita income due to its small population and substantial GDP. Despite economic challenges post-war, Kuwait has maintained a low inflation rate and a diverse import market for food and construction materials. The government has sought advice from international financial institutions to implement economic reforms focusing on privatization and tax increases. Kuwait"s strategic location enhances its role as a trade hub in the region, with major trading partners including the US, Japan, South Korea, and several European nations.
-
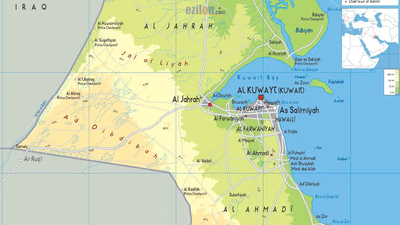
Kuwait"s ports play a crucial role in its trade landscape, with the Port of Shuwaikh being the largest and busiest, handling a variety of commercial cargo. The Port of Shuaiba follows as the second-largest, focusing on bulk cargo such as petroleum products and chemicals. Bubiyan Port, currently under development, aims to become a significant transshipment hub with advanced facilities. Al-Ahmadi Port is dedicated to oil exports, while other ports like Al-Zour and Doha serve specific functions in the oil and light goods sectors. The strategic location of these ports enhances Kuwait"s attractiveness for global traders. Import regulations require licenses from the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, ensuring that only registered importers can operate within the country. This regulatory framework supports a stable trade environment, fostering connections between local exporters and international markets.
-
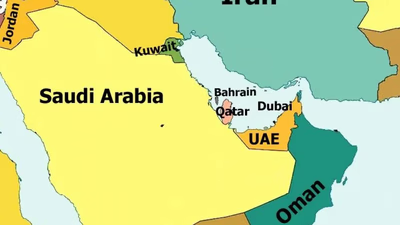
Kuwait, located in West Asia, shares borders with Saudi Arabia and Iraq, and has a coastline along the Persian Gulf. Despite its small geographical size of over 17,000 square kilometers, Kuwait has a rich history and complex identity. The country was founded by Sheikh Barak ibn Gharir al-Hamid in the early 18th century and has evolved into a significant player in regional trade. Approximately 60% of its population are Arabs, with a notable Asian demographic as well. The official language is Arabic, while English is widely spoken due to historical influences. Kuwait"s climate is predominantly hot and dry, necessitating substantial imports of food and water. The nation has made strides in improving its agricultural practices through greenhouses and other innovations. Politically, Kuwait operates as a sheikhdom with a parliamentary system that allows for greater openness compared to some neighboring countries.
Since gaining independence in 1961, it has maintained stability and fostered international relations despite historical territorial disputes with Iraq. Today, Kuwait stands as one of the safest countries in the region, making it an attractive hub for trade and business networking. "






