Egypt"s agriculture and Suez Canal boost trade opportunities. "
Agriculture has traditionally played a significant role in Egypt's economy. The country benefits from the fertile soil of the Nile River, allowing for the cultivation of a variety of crops such as cotton, wheat, corn, sugarcane, and fruits. Agriculture contributes to both domestic consumption and exports, providing employment opportunities for a significant portion of the population. The Suez Canal is a vital source of income for Egypt. It is an artificial waterway connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea, allowing for shorter trade routes between Europe and Asia. The canal generates substantial revenue through tolls and fees paid by ships passing through, making it a crucial contributor to Egypt's economy.
Egypt's economic situation grew by 0.26% in 2020. The country has a gross domestic product of $ 332.90 billion. About 28 million people are working in this country, and of course, the participation rate has increased. Estimates show that Egypt's GDP is estimated at more than 32% in the agricultural sector. Egypt produces 688,100 barrels of oil per day. The country as a whole has a lot of gas resources and 76.40 billion cubic meters of gas is produced during the year. Exports in Egypt mostly include crude oil and petrochemical products, and of course cotton, textiles and hardware are also exported from this country to other countries.
Egypt has a diverse manufacturing sector, including textiles, chemicals, food processing, automotive, and construction materials. Industrial production contributes to the country's economic growth and employment. Additionally, Egypt has been striving to attract foreign direct investment (FDI) in various sectors to boost industrialization and stimulate economic development. Egyptians working abroad, particularly in Arab Gulf countries, contribute significantly to the country's income through remittances. These funds sent back home by expatriate workers support households and contribute to domestic consumption.
It is clear that in the newest export sectors of Egypt, hardware, as well as chemicals, can be seen. Egyptian imported products mostly include machinery, equipment, and food. Also, chemicals and timber are considered as other imported items. The economic situation of Egypt is being seriously monitored, and of course, the situation of the annual GDP growth rate in Egypt is estimated at 7.70%. The situation of GDP in Egypt is pursued at a certain value. GDP at constant prices in Egypt has also increased by more than 90%.
Egypt receives financial assistance and investment from international organizations, countries, and multinational corporations. This aid and investment can come in the form of grants, loans, or direct investment in sectors such as infrastructure, energy, and social development projects. Egypt's services sector, including banking, finance, telecommunications, and information technology, plays an important role in the economy. Cairo, the capital city, hosts the headquarters of major banks and financial institutions, serving as a regional hub for finance and business activities.
GDP per capita in this country has also grown by 3%. Gross domestic product from agriculture in Egypt has grown by 12 percent, while the GDP of construction in this country is estimated at 1 percent. It is clear that the GDP policies of the mines in this country have grown by 10%, and the Egyptian economy, which is dependent on the GDP of the public transport sector, is also growing by 4%. Of course, the financial and income sources in this country are seriously pursued and the state of economic growth in this country is evaluated at constant values. In this country in general, the government has tried to adopt modern mechanisms. The Egyptian economy is being seriously pursued in the export sector, and the amount of exports in this country has changed periodically, although the domestic economic values in this country have also improved.
Egypt is a significant producer and exporter of oil and natural gas in the region. The country has both onshore and offshore oil and gas fields, with major reserves located in the Nile Delta and the Mediterranean Sea. Revenue from the extraction and export of oil and gas resources contributes significantly to Egypt's income and foreign exchange earnings. Egypt's rich historical and cultural heritage, including iconic landmarks such as the Pyramids of Giza, the Sphinx, and ancient temples, attracts millions of tourists each year. Tourism is a vital sector for the Egyptian economy, providing employment opportunities and generating foreign currency through visitor expenditures.
-

Egypt"s population exceeds 100 million, providing a vast labor force and consumer market for businesses. This demographic advantage allows companies to access a diverse talent pool and cater to a significant domestic market. The growing middle class and increasing disposable income present opportunities for both local and international firms to expand their operations. Companies contribute to job creation, addressing unemployment while boosting economic development. The corporate tax rate stands at approximately 25%, with personal income tax rates varying from 22. 5% to 34%. Sales tax has increased from 10% to 14%, while social security remains stable at around 40%. Egypt"s strategic location in northeastern Africa, bordered by Libya, Sudan, the Mediterranean Sea, Israel, and Palestine, enhances its trade potential.
The country"s rich cultural heritage and historical significance attract tourism and investment. Companies operating in Egypt not only generate revenue but also invest in employee training, enhancing workforce skills and employability. This investment fosters long-term economic growth and improved living standards for the population. "
-
Egypt"s economy is diverse and strategically located, making it a vital trade partner in the Middle East. Key sectors include agriculture, manufacturing, services, and energy. The country imports a variety of goods such as agricultural products, machinery, chemicals, and consumer items. Trade with Egypt supports economic growth by facilitating development projects and enhancing market access. Its geographical position near the Suez Canal further boosts its importance in global trade routes. Despite political challenges and external pressures, particularly from the US regarding Iran-Egypt relations, Egypt remains a promising destination for exports due to its large market size and economic potential. The country’s non-oil export strategies are crucial for expanding trade relations with regional partners like Iran. While there are hurdles such as tariffs and regulatory issues, ongoing reforms aim to improve the business environment for foreign investors.
Overall, engaging in trade with Egypt not only benefits individual economies but also contributes to regional stability and development. "
-

Egypt stands as a pivotal economic force in the MENA region, characterized by its strategic location and diverse economy. The country boasts a well-developed financial sector, with Cairo serving as a hub for banking and financial services. The Egyptian Exchange attracts both domestic and international investors, reflecting the country"s robust economic framework. Egypt"s active participation in international trade is underscored by its membership in the WTO and various trade agreements with key partners like the EU, Arab nations, the US, and China. The Suez Canal enhances Egypt"s significance in global maritime trade. Recent economic indicators show positive growth trends in import-export sectors and foreign direct investment (FDI), alongside ongoing government reforms aimed at improving the business environment. Despite challenges such as foreign debt and fluctuating currency values, Egypt"s commitment to attracting investment in energy, infrastructure, and manufacturing remains strong. Additionally, tourism plays a crucial role in the economy, contributing significantly to foreign exchange earnings.
Overall, Egypt"s strategic initiatives position it favorably within regional trade dynamics. "
-

Cairo, the capital of Egypt, serves as the political, economic, and cultural center of the nation. With a population exceeding 20 million, it is one of Africa"s largest cities. Cairo is renowned for its historical landmarks such as the Great Pyramids of Giza and the Egyptian Museum. The city boasts modern infrastructure alongside its rich heritage. Alexandria, Egypt"s second-largest city, is known for its Mediterranean charm and historical sites like the Citadel of Qaitbay. Giza is famous for its pyramids and attracts numerous tourists. Other notable cities include Port Said, recognized for its luxurious atmosphere; Suez, a hub for investment; and Luxor, often called the world"s largest open-air museum due to its ancient temples and tombs. The Greater Cairo area significantly contributes to Egypt"s GDP and houses most private sector services.
Despite calls for decentralization, government functions remain concentrated in Cairo. The city also has a thriving informal economy that employs a large portion of its workforce. Aswan, located near Sudan, is known for its agricultural significance due to the Nile River and features attractions like Nubian villages and temples. Overall, Egypt"s cities offer diverse economic opportunities and cultural experiences. "
-

Egypt"s economy is significantly influenced by agriculture, particularly due to the fertile Nile River, which supports the cultivation of crops like cotton and wheat. The Suez Canal is another critical economic asset, generating substantial revenue through tolls from ships. In 2020, Egypt"s GDP grew by 0. 26%, with a total GDP of $332. 90 billion and a notable contribution from the agricultural sector, estimated at over 32%. The country also produces significant amounts of oil and gas, with daily oil production at 688,100 barrels and annual gas production at 76. 40 billion cubic meters. Exports primarily consist of crude oil, petrochemicals, textiles, and hardware.
The manufacturing sector is diverse, encompassing textiles to automotive production. Foreign direct investment (FDI) is actively sought to enhance industrialization and economic growth. Remittances from Egyptians working abroad play a crucial role in supporting domestic consumption. The services sector, including banking and telecommunications, is vital for economic stability. Recent growth rates indicate a positive trend in GDP per capita and various sectors such as agriculture and construction are also experiencing growth. Egypt"s rich cultural heritage boosts tourism, further contributing to the economy by generating foreign currency. "
-
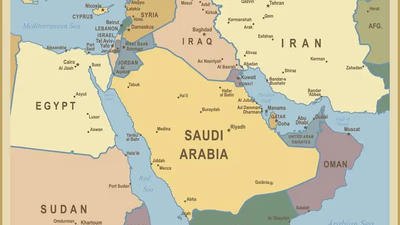
Egypt"s geographical position in northeastern Africa, bordered by Libya, Sudan, the Mediterranean Sea, Israel, and Palestine, influences its climate and economy. The northern region enjoys a temperate climate due to the Mediterranean, while the eastern and western deserts experience extreme temperatures. Economic indicators show a mixed performance; construction contributes 1% to GDP, while mining has seen a 10% growth. The public transport sector also shows a positive trend with a 4% increase. However, the current account balance has faced challenges with a negative GDP situation in recent years. Import and export sectors have shown growth rates of 7% and 3%, respectively. Despite these fluctuations, foreign debt has risen by 9%, and tax rates have increased significantly over time. Cultural traditions in Egypt are evolving, reflecting the complexities of its society. "
-

Egypt"s economy is characterized by a GDP of $332. 90 billion, with significant contributions from agriculture, oil, and gas sectors. Approximately 28 million people are employed, with a notable increase in participation rates. The agricultural sector accounts for over 32% of GDP, while oil production stands at 688,100 barrels per day and gas production reaches 76. 40 billion cubic meters annually. Key exports include crude oil, petrochemicals, cotton, textiles, and hardware. Imports primarily consist of machinery, equipment, food products, chemicals, and timber. The annual GDP growth rate is estimated at 7.
70%, with notable increases in various sectors such as agriculture (12%) and mining (10%). Egypt operates under a republican political structure where the president is elected every six years by popular vote. The People"s Council (Majlis al-Shabi) consists of 454 members; most are elected by the public while others are appointed by the president. The prime minister is appointed by the president and leads the cabinet. An advisory council known as Al-Shura also plays a role in governance with its own elected members.
-

Egypt"s rich cultural heritage is deeply rooted in its ancient civilization, characterized by iconic pyramids and temples. The country celebrates its pharaonic past through various festivals and museums, while the Arabic language, particularly the Egyptian dialect, plays a crucial role in daily life. Egyptian cuisine reflects diverse influences, featuring dishes like ful medames and koshari. Recent improvements in healthcare and economic structures have enhanced the quality of life for many Egyptians. The political landscape remains stable, with efforts to minimize corruption and improve social security. However, strict laws govern social interactions and respect for cultural beliefs. Egypt"s economy is diverse, with significant contributions from agriculture and industry, particularly in cement and food production. Despite potential trade opportunities with countries like Iran, political tensions hinder full economic collaboration. Family values are central to Egyptian society, emphasizing strong kinship ties and traditional gender roles.