
Fossil trading involves verified exporters and importers in Asia.
Fossil supply and demand and trade in international markets is a complex area that is affected by many factors. Demand for fossils in international markets depends on various factors. Some important factors include interest in natural history, paleontology, education and research, collection and exhibits, home decorations, and fossil related products. Also, the demand may also vary based on the type of fossil, for example, some types of fossils such as dinosaurs or various animals are more attractive to collectors and enthusiasts.
The first and most important thing for a fossil dealer is to have sufficient knowledge in the field of paleontology. This includes knowing the types of fossils, their extraction and preservation methods, the history and formation of fossils, as well as knowing the samples exposed to fraud and fakes. A fossil trader must have the ability to research fossils. This includes examining the fossil market, pricing, market trends, fossil history and knowing about famous mining sites. A fossil trader must know the fossil market well. This includes knowing about the possible buyers and sellers, competition, traders and collections related to the fossil industry. A fossil trader must have financial management skills. This includes financial planning, managing expenses and income, recording and documenting transactions, and the ability to manage finances on a small and large scale.
Each country has its own laws and regulations in the field of fossil export, import and trade. The fossil stone trader must be familiar with these rules and perform his actions carefully. In addition, one needs to be aware of restrictions and prohibitions on specific fossils in countries. Having a strong network and connections in the fossil industry is very important for a fossil trader. This includes communicating with farmers, paleontologists, other traders and potential customers. A fossil dealer must be able to identify the original fossils. This includes the ability to detect fake, altered and non-genuine fossils. For this purpose, the businessman must be familiar with the methods and techniques of identifying original fossils and have the ability to distinguish between original and fake fossils.
The fossil dealer must have sufficient knowledge in the field of preservation and display of fossils. This includes the ability to keep the fossils in the right conditions to maintain their value and quality, perform necessary cleaning and repairs on the fossils , as well as the ability to display and present the fossils in a beautiful and attractive way to the customers. A fossil dealer must have the ability to properly evaluate and price fossils. This includes the ability to estimate a price based on the fossil's characteristics, its historical and scientific value, and its current market value. Fossil stone trader must have the ability to choose and buy high-quality and suitable fossils. This includes the ability to identify and evaluate high-quality fossils, recognize suitable buying opportunities, negotiate and negotiate with vendors.
Fossils are mainly extracted from areas that have masses and rock layers with the richest fossils. Areas such as East Africa, South America, Asia and Australia have rich fossil mines. Also, fossils may be accidentally obtained through construction, road construction and excavations in the fields. Each country has its own laws and regulations in the field of export, import and trade of fossils. Some countries may impose restrictions and bans on the trade of certain fossils, especially if the fossils belong to endangered or protected species. Fossil stone traders should be familiar with the laws and regulations related to the export and import of fossils in different countries and plan their actions accordingly.
-

Fossils can hold significant economic value, but their worth often varies based on several factors. The type and quality of a fossil are crucial in determining its price; well-preserved specimens with intricate details command higher prices. Size also plays a role, as larger fossils are typically rarer and more sought after. Rarity is a key factor; unique fossils attract collectors and institutions, driving up their market value. Legal regulations surrounding fossil extraction and trade can influence pricing across different regions. Notable examples of valuable fossils include amber specimens containing ancient insects, the famous Sue dinosaur fossil, and the Guinness Gold Leaf fossil leaves used in art. Demand and supply dynamics further affect pricing; high demand coupled with low supply usually results in increased prices. Fossils can be traded in virtual markets where auction dynamics come into play.
Beyond economic value, many fossils possess scientific significance, aiding research into Earth"s history and evolution. Some serve as cultural artifacts or symbols within museums, while others represent mineral resources like oil or coal. Overall, the pricing of fossils is complex and influenced by various market factors. "
-
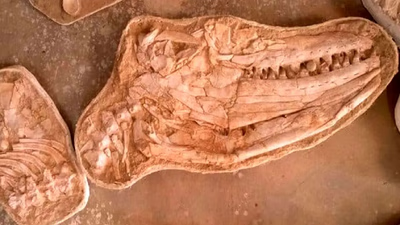
Selling fossils internationally requires careful consideration of legal regulations and market dynamics. Sellers should seek reliable buyers and utilize written contracts to ensure clarity in transactions. Fossils can be sold through various channels, including fairs, auctions, and online platforms. Compliance with local laws regarding fossil protection is crucial during export. To establish authenticity, consulting paleontologists or experts is recommended, as they can provide necessary evaluations and certificates of authenticity. For instance, a farmer in Turkey looking to sell a fossil to a buyer in Germany must first assess the fossil"s value with expert help. Researching potential buyers and setting a competitive price based on market trends is essential. Communication with the buyer should be clear, covering details about the fossil and transaction terms.
Payment methods must ensure security, while transportation arrangements must comply with regulations to avoid legal issues. Buyers should also conduct due diligence by verifying the seller"s credibility and requesting documentation that proves the fossil"s authenticity. This includes checking the seller"s history and possibly visiting their location for assurance. Overall, both parties must prioritize transparency and legality throughout the transaction process.
-

Fossil rock discovery in the Middle East and West Asia varies significantly due to geological, geographic, and historical factors. Regions like Iran, Saudi Arabia, and Turkey showcase diverse fossil types influenced by their unique geochemical conditions. In Iran, notable areas such as Khuzestan and Kerman yield fossils like ammonites and trilobites. Saudi Arabia"s Jabal al-Louz and Hael regions also reveal significant fossil finds, including bivalites and coal rocks. Turkey"s Anatolian region is rich in fossil diversity, with similar finds of ammonites and trilobites. However, some areas face challenges in fossil preservation due to geological processes like erosion and climate changes. Cultural and economic factors also play a role; countries investing in geological research are more likely to discover fossils. Overall, while certain regions are prolific in fossil findings, others may experience scarcity due to a combination of environmental conditions and resource allocation.
-

Fossil trade in international markets is influenced by various factors, including demand driven by interests in natural history, paleontology, and home decor. The appeal of specific fossils, such as dinosaurs, significantly impacts collector interest. Knowledge of paleontology is crucial for fossil dealers, who must understand fossil types, extraction methods, and preservation techniques. Research skills are essential for analyzing market trends and pricing while being aware of competition and potential buyers. Financial management is also vital for tracking expenses and income effectively. Each country has distinct regulations governing fossil trade, necessitating familiarity with export and import laws to avoid legal issues. Building a strong network within the fossil industry enhances opportunities for traders to connect with paleontologists and customers. Identifying genuine fossils from fakes is critical; thus, traders must be adept at evaluating authenticity.
Proper preservation techniques are necessary to maintain the quality of fossils for display and sale. Additionally, traders should be skilled in pricing based on historical significance and market value while recognizing high-quality specimens during procurement.




